| Solar System Dynamics & Planetology Group |
 |
C/1955 G1 Abell |  |
| Solar System Dynamics & Planetology Group |
 |
C/1955 G1 Abell |  |
| number of observations | 35 |
| number of residuals | 63 |
| data interval | 1955 Apr. 13 — 1956 Apr. 30 |
| rms [arcsec] | 1.00 |
| orbit quality class | 1b |
| Epoch (TT) | 19540408.0 | = JD 2434840.5 |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19540324.114918 | ± 0.011720 |
| perihelion distance | 4.49562524 | ± 0.00010953 |
| eccentricity | 1.00279180 | ± 0.00007595 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 73.749143 | ± 0.001855 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 321.334541 | ± 0.000335 |
| inclination [deg] | 123.932726 | ± 0.000280 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | -621.00 | ± 16.90 |
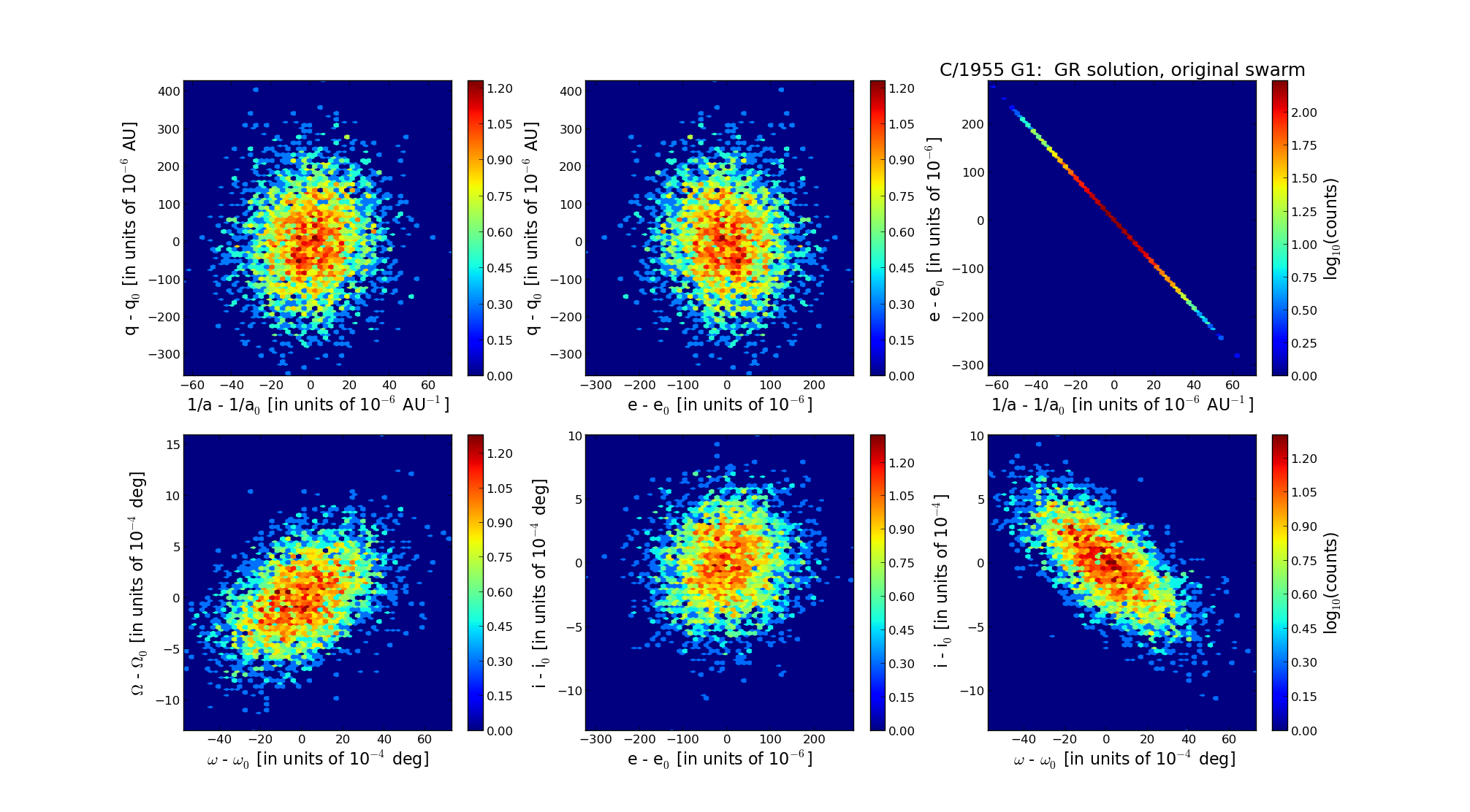
| Epoch (TT) | 16490116 | |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19540325.000609 | ± 0.011929 |
| perihelion distance | 4.49692869 | ± 0.00010950 |
| eccentricity | 0.99963621 | ± 0.00007649 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 73.796250 | ± 0.001859 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 321.294299 | ± 0.000333 |
| inclination [deg] | 123.952116 | ± 0.000276 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | 80.90 | ± 17.01 |
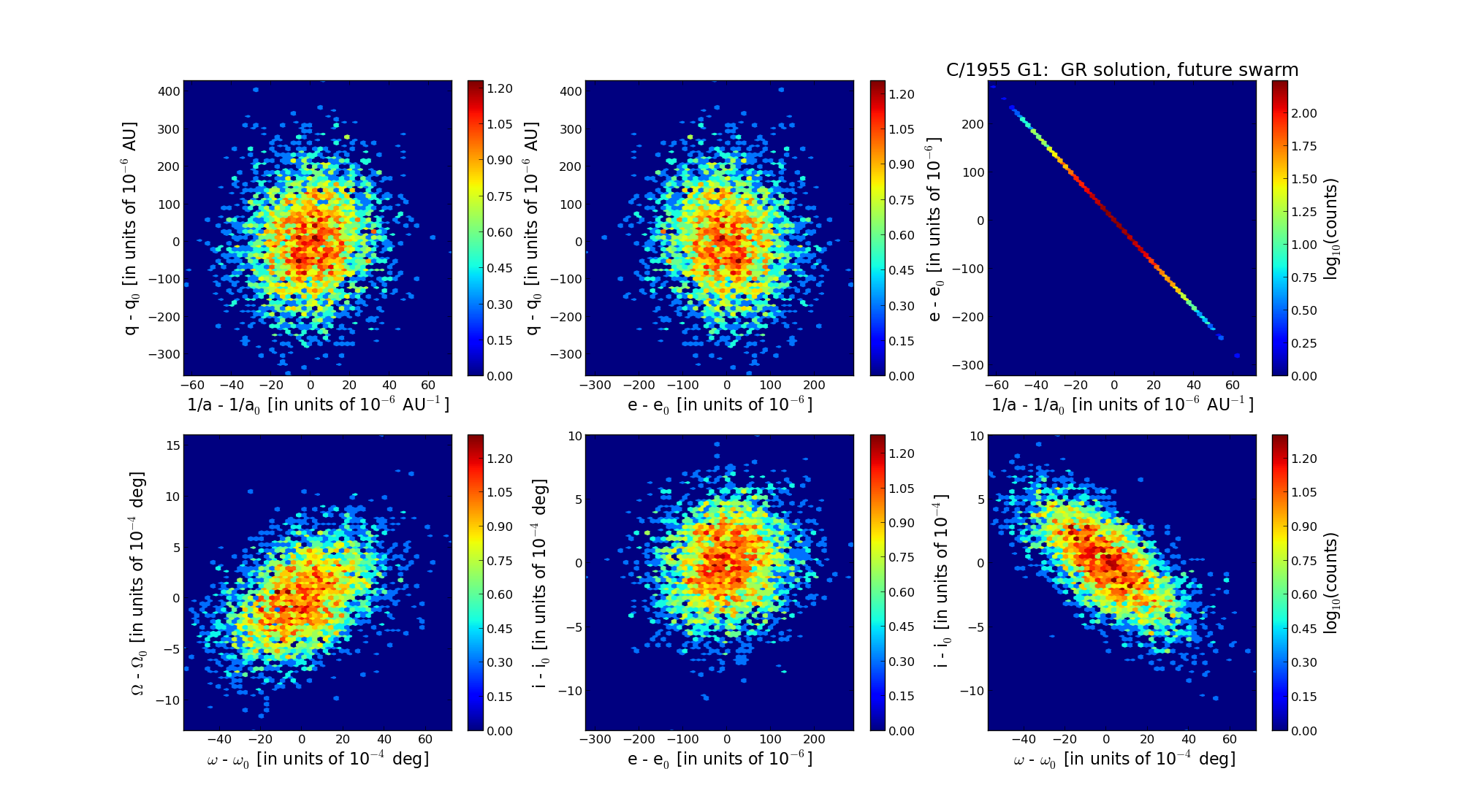
| Epoch (TT) | 22580414 | |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19540325.394275 | ± 0.011617 |
| perihelion distance | 4.49578851 | ± 0.00010951 |
| eccentricity | 1.00009459 | ± 0.00007642 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 73.779413 | ± 0.001858 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 321.311236 | ± 0.000334 |
| inclination [deg] | 123.923277 | ± 0.000275 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | -21.04 | ± 17.00 |