| Solar System Dynamics & Planetology Group |
 |
C/1921 E1 Reid |  |
| Solar System Dynamics & Planetology Group |
 |
C/1921 E1 Reid |  |
| number of observations | 568 |
| number of residuals | 914 |
| data interval | 1921 Mar. 15 — 1921 Nov. 26 |
| rms [arcsec] | 3.27 |
| orbit quality class | 2a |
| Epoch (TT) | 19210421.0 | = JD 2422800.5 |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19210510.449383 | ± 0.000308 |
| perihelion distance | 1.00845704 | ± 0.00000145 |
| eccentricity | 1.00049609 | ± 0.00003777 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 64.491010 | ± 0.000236 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 269.440232 | ± 0.000293 |
| inclination [deg] | 132.187612 | ± 0.000113 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | -491.93 | ± 37.46 |
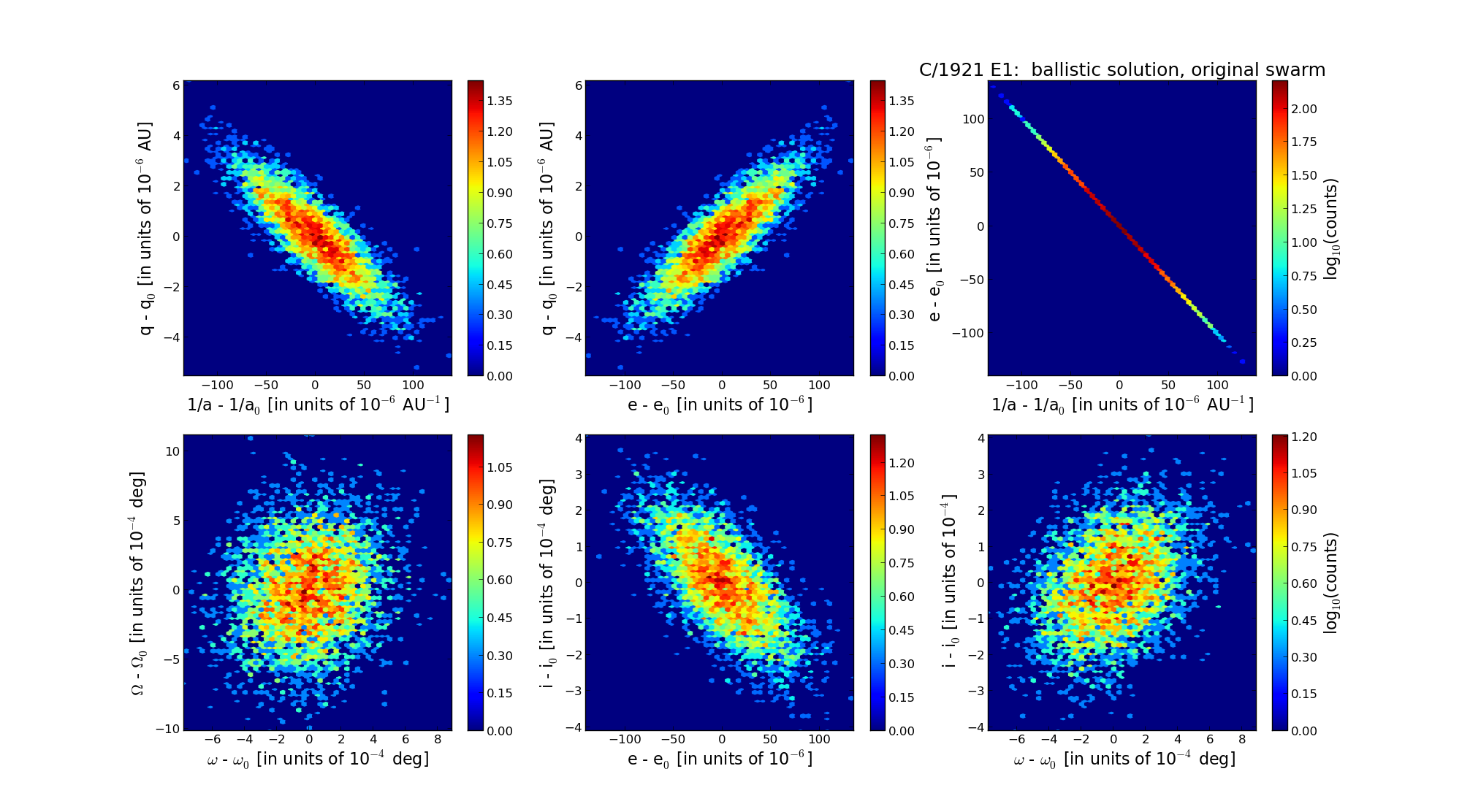
| Epoch (TT) | 16240706 | |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19210510.690297 | ± 0.000189 |
| perihelion distance | 1.00693074 | ± 0.00000143 |
| eccentricity | 1.00012096 | ± 0.00003788 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 64.705467 | ± 0.000237 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 269.587562 | ± 0.000307 |
| inclination [deg] | 132.180302 | ± 0.000115 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | -120.12 | ± 37.62 |
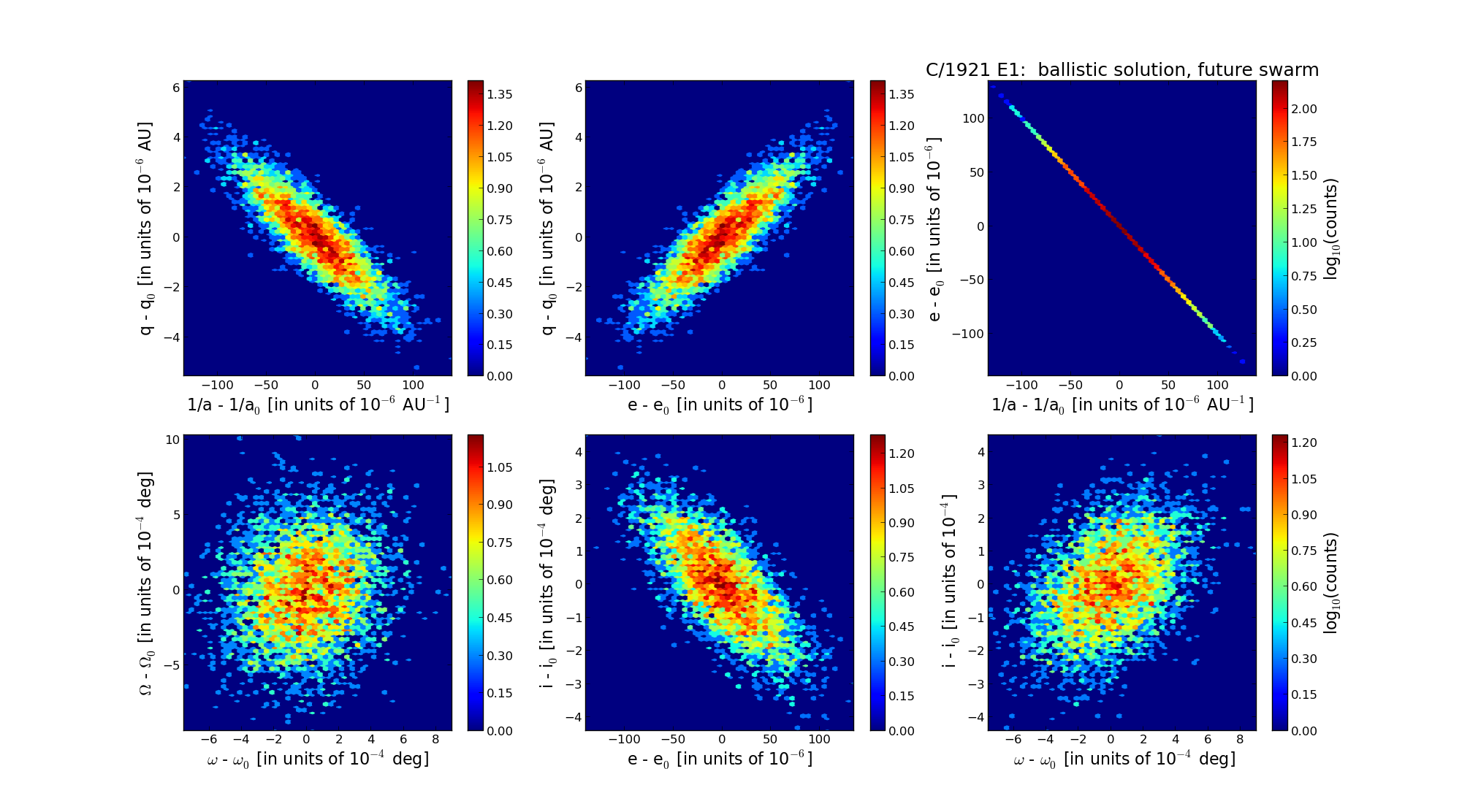
| Epoch (TT) | 22140224 | |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19210510.725714 | ± 0.000333 |
| perihelion distance | 1.00362490 | ± 0.00000145 |
| eccentricity | 1.00049067 | ± 0.00003778 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 64.338847 | ± 0.000239 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 269.351069 | ± 0.000282 |
| inclination [deg] | 132.108442 | ± 0.000123 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | -488.90 | ± 37.64 |
| number of observations | 568 |
| number of residuals | 914 |
| data interval | 1921 Mar. 15 — 1921 Nov. 26 |
| rms [arcsec] | 3.25 |
| orbit quality class | 2a |
| Epoch (TT) | 19210421.0 | = JD 2422800.5 |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19210510.453240 | ± 0.000810 |
| perihelion distance | 1.00843659 | ± 0.00000434 |
| eccentricity | 1.00018145 | ± 0.00007412 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 64.493716 | ± 0.000563 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 269.438264 | ± 0.000509 |
| inclination [deg] | 132.188366 | ± 0.000185 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | -179.93 | ± 73.50 |
| Nongravitational parameters [10-8 au/day2] | A1 = 3.155 ± 0.629 | A2 = -0.451 ± 0.861 | A3 = 0.0 (assumed) |
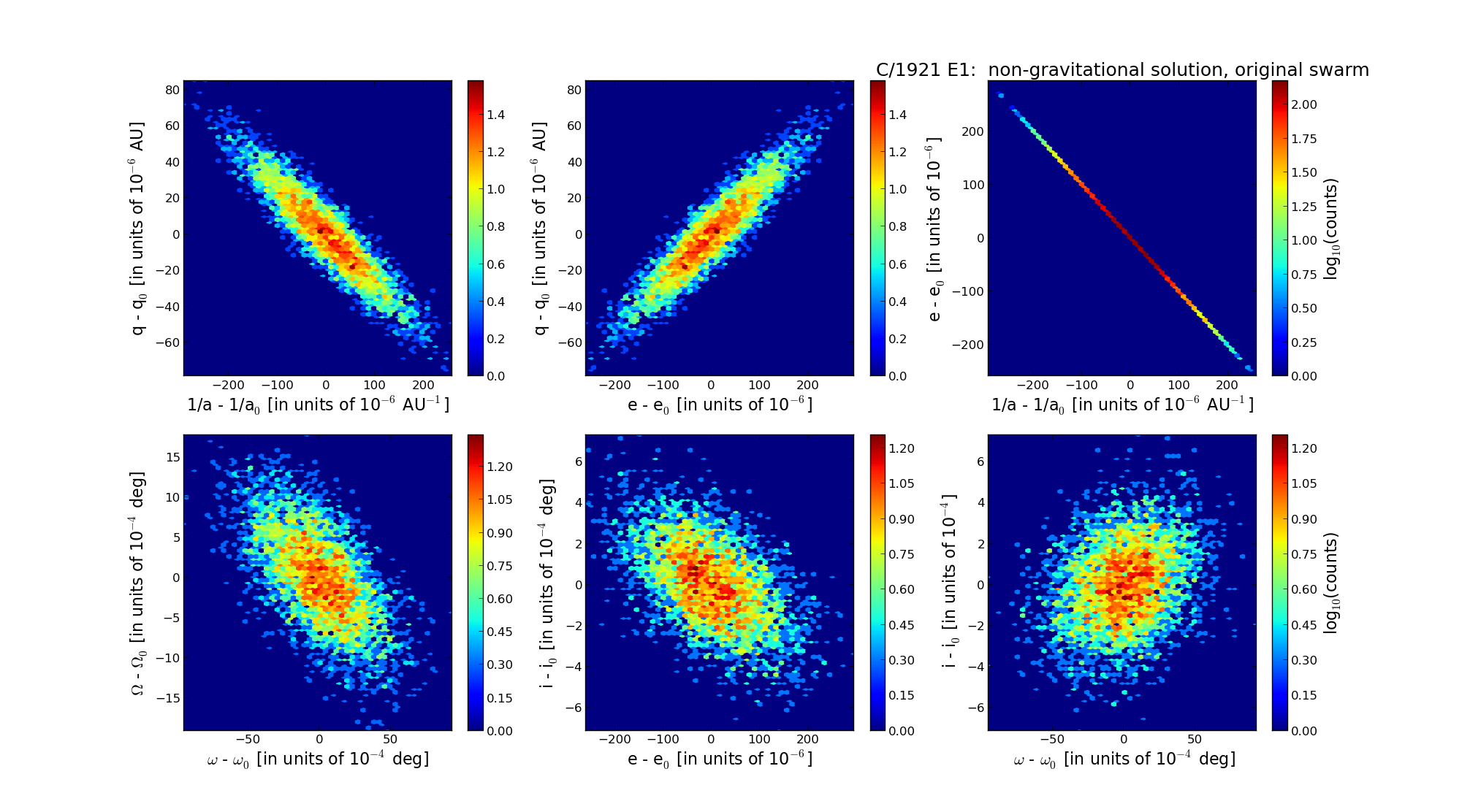
| Epoch (TT) | 16220319 | |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19210510.691603 | ± 0.001631 |
| perihelion distance | 1.00687747 | ± 0.00002269 |
| eccentricity | 0.99991349 | ± 0.00008135 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 64.710041 | ± 0.002463 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 269.585493 | ± 0.000538 |
| inclination [deg] | 132.181074 | ± 0.000188 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | 85.92 | ± 80.79 |
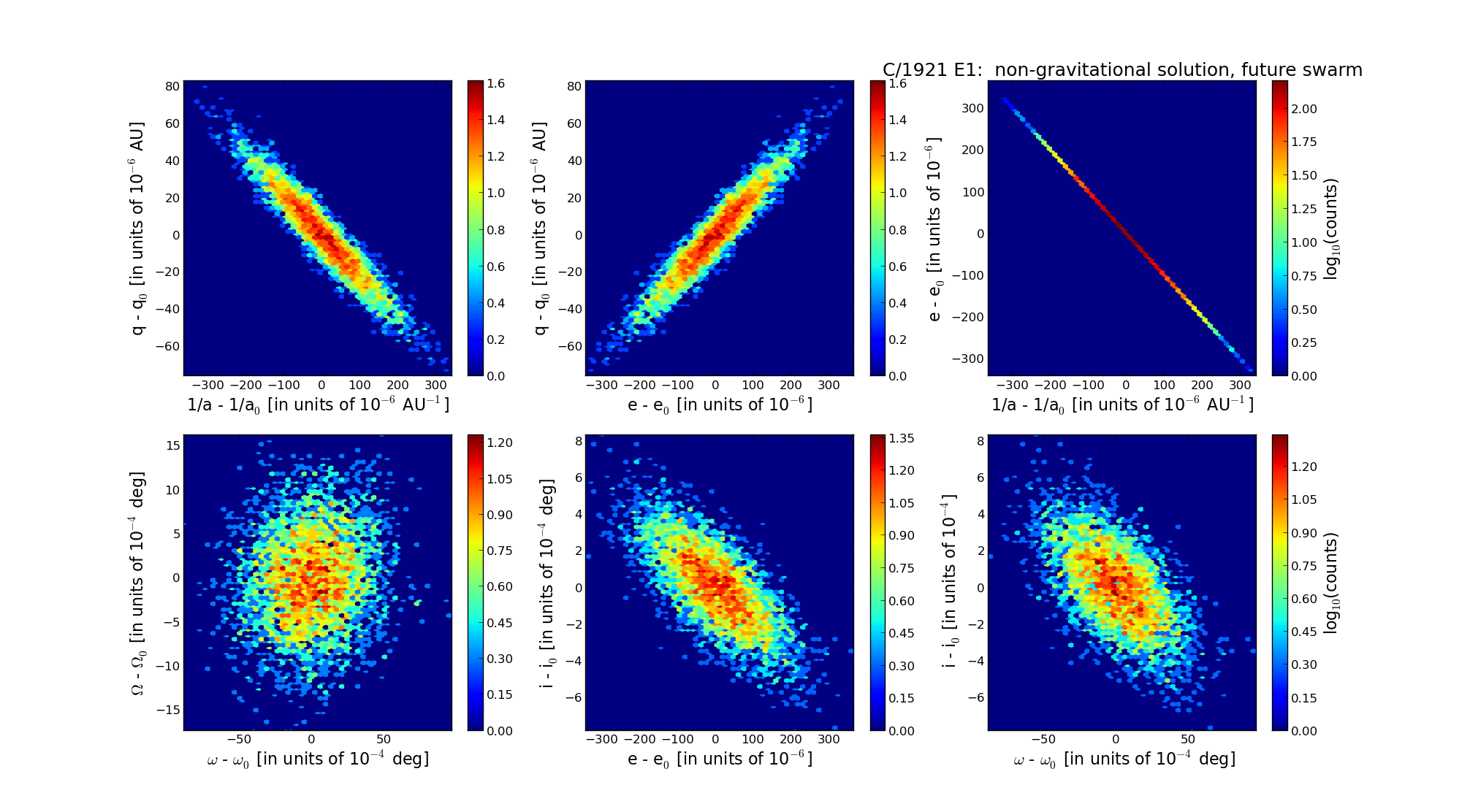
| Epoch (TT) | 22170320 | |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19210510.725850 | ± 0.001774 |
| perihelion distance | 1.00355226 | ± 0.00002192 |
| eccentricity | 1.00021161 | ± 0.00009695 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 64.332073 | ± 0.002368 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 269.349172 | ± 0.000497 |
| inclination [deg] | 132.109300 | ± 0.000210 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | -210.87 | ± 96.60 |