| Solar System Dynamics & Planetology Group |
 |
C/1913 Y1 Delavan |  |
| Solar System Dynamics & Planetology Group |
 |
C/1913 Y1 Delavan |  |
| number of observations | 1006 |
| number of residuals | 1874 |
| data interval | 1913 Dec. 18 — 1915 Sep. 7 |
| rms [arcsec] | 2.06 |
| orbit quality class | 1a |
| Epoch (TT) | 19141104.0 | = JD 2420440.5 |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19141026.767056 | ± 0.000062 |
| perihelion distance | 1.10445641 | ± 0.00000079 |
| eccentricity | 1.00016199 | ± 0.00000143 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 97.467346 | ± 0.000028 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 60.396107 | ± 0.000024 |
| inclination [deg] | 68.038294 | ± 0.000042 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | -146.67 | ± 1.29 |
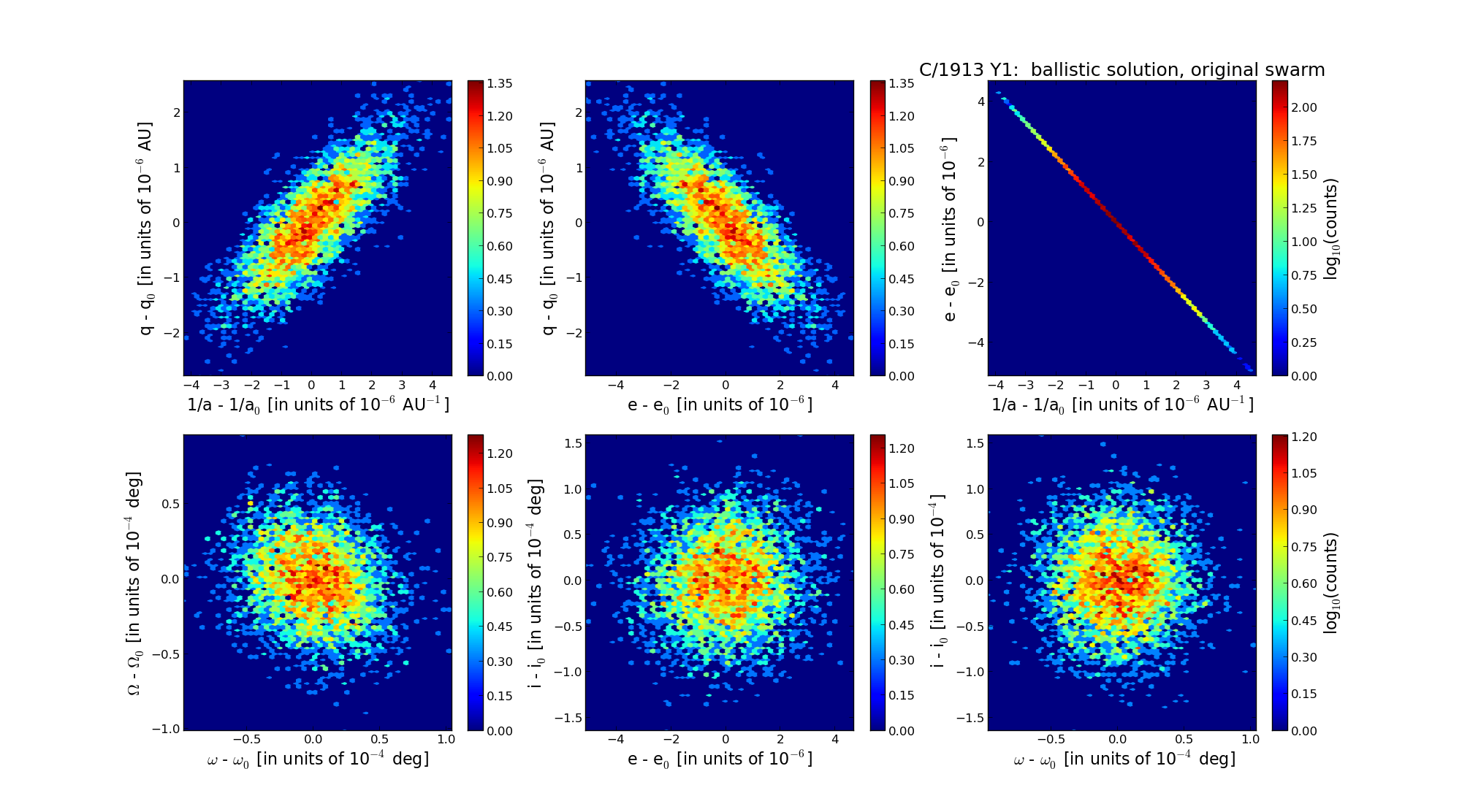
| Epoch (TT) | 16160310 | |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19141025.816829 | ± 0.000055 |
| perihelion distance | 1.10070306 | ± 0.00000079 |
| eccentricity | 0.99997563 | ± 0.00000143 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 97.539554 | ± 0.000028 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 60.475762 | ± 0.000024 |
| inclination [deg] | 67.986327 | ± 0.000043 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | 22.14 | ± 1.30 |
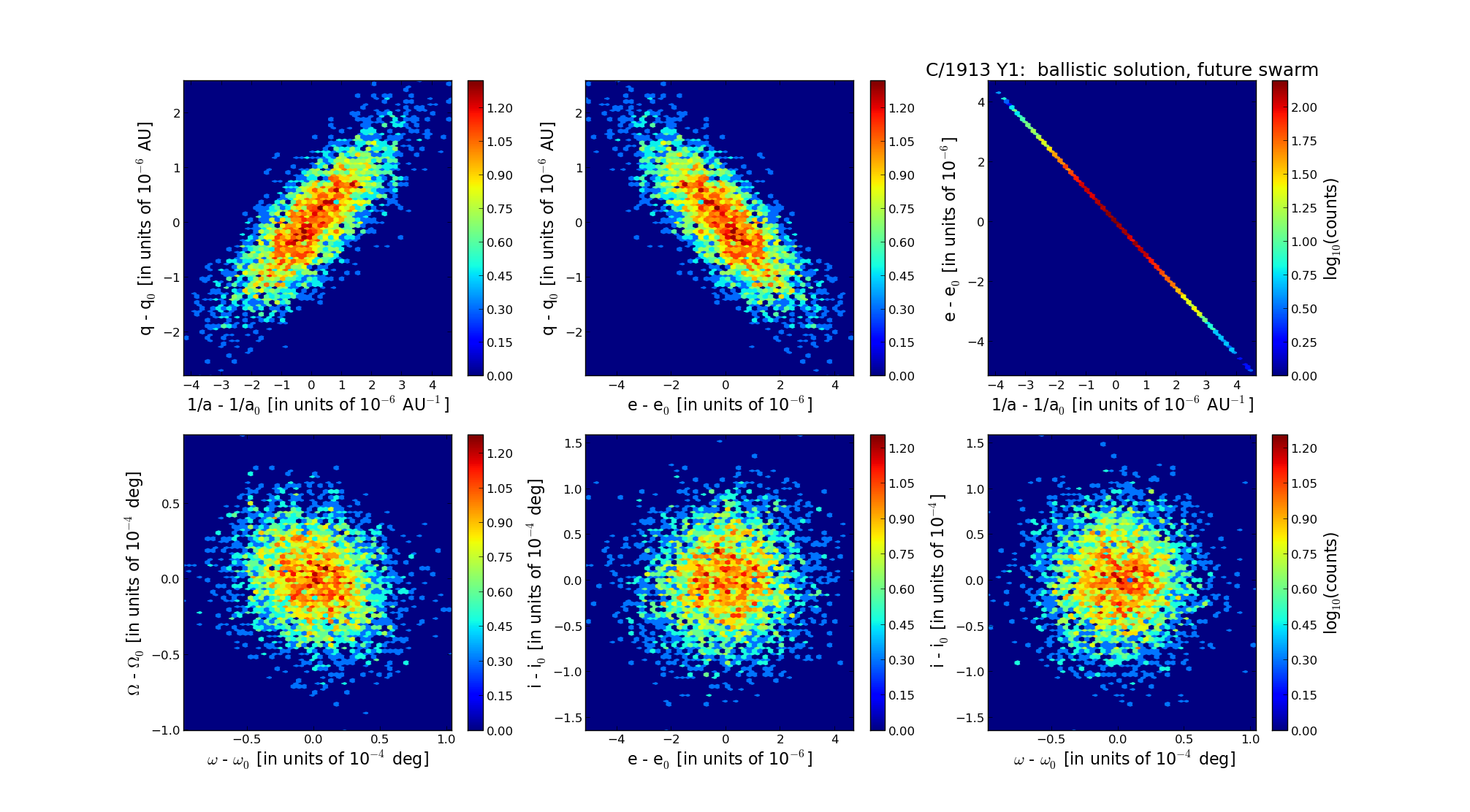
| Epoch (TT) | 22131027 | |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19141026.924754 | ± 0.000074 |
| perihelion distance | 1.10518625 | ± 0.00000079 |
| eccentricity | 0.99993766 | ± 0.00000143 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 97.460986 | ± 0.000028 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 60.292940 | ± 0.000024 |
| inclination [deg] | 67.982189 | ± 0.000043 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | 56.41 | ± 1.30 |
| number of observations | 1006 |
| number of residuals | 1860 |
| data interval | 1913 Dec. 18 — 1915 Sep. 7 |
| rms [arcsec] | 2.00 |
| orbit quality class | 1b |
| Epoch (TT) | 19141104.0 | = JD 2420440.5 |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19141026.767012 | ± 0.000062 |
| perihelion distance | 1.10444242 | ± 0.00000218 |
| eccentricity | 1.00009618 | ± 0.00000906 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 97.467000 | ± 0.000059 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 60.396112 | ± 0.000023 |
| inclination [deg] | 68.038602 | ± 0.000059 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | -87.08 | ± 8.20 |
| Nongravitational parameters [10-8 au/day2] | A1 = 1.240 ± 0.172 | A2 = 0.0 (assumed) | A3 = 0.0 (assumed) |
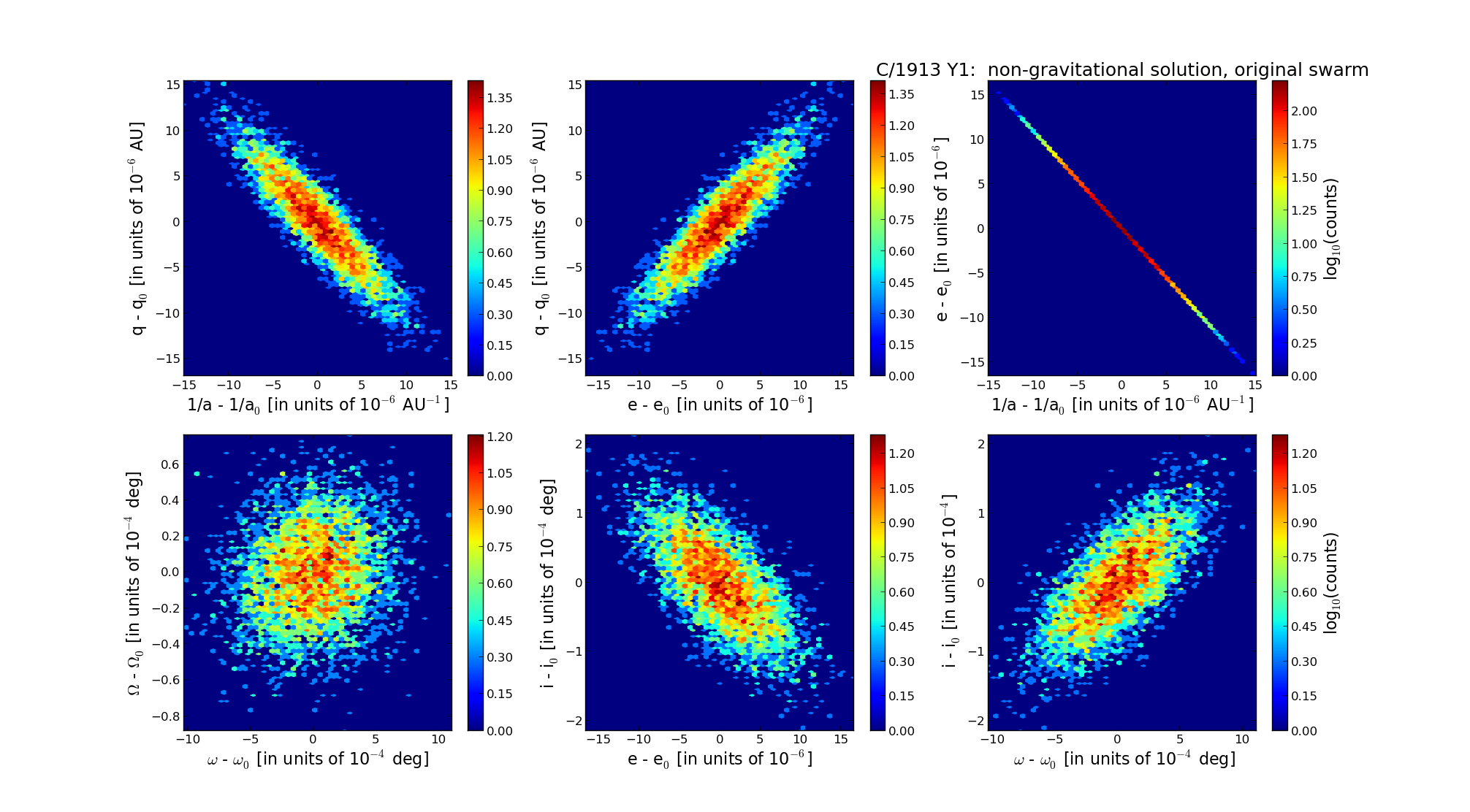
| Epoch (TT) | 16151111 | |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19141025.817363 | ± 0.000089 |
| perihelion distance | 1.10067114 | ± 0.00000461 |
| eccentricity | 0.99994214 | ± 0.00000465 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 97.541763 | ± 0.000303 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 60.475772 | ± 0.000024 |
| inclination [deg] | 67.986634 | ± 0.000059 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | 52.57 | ± 4.23 |
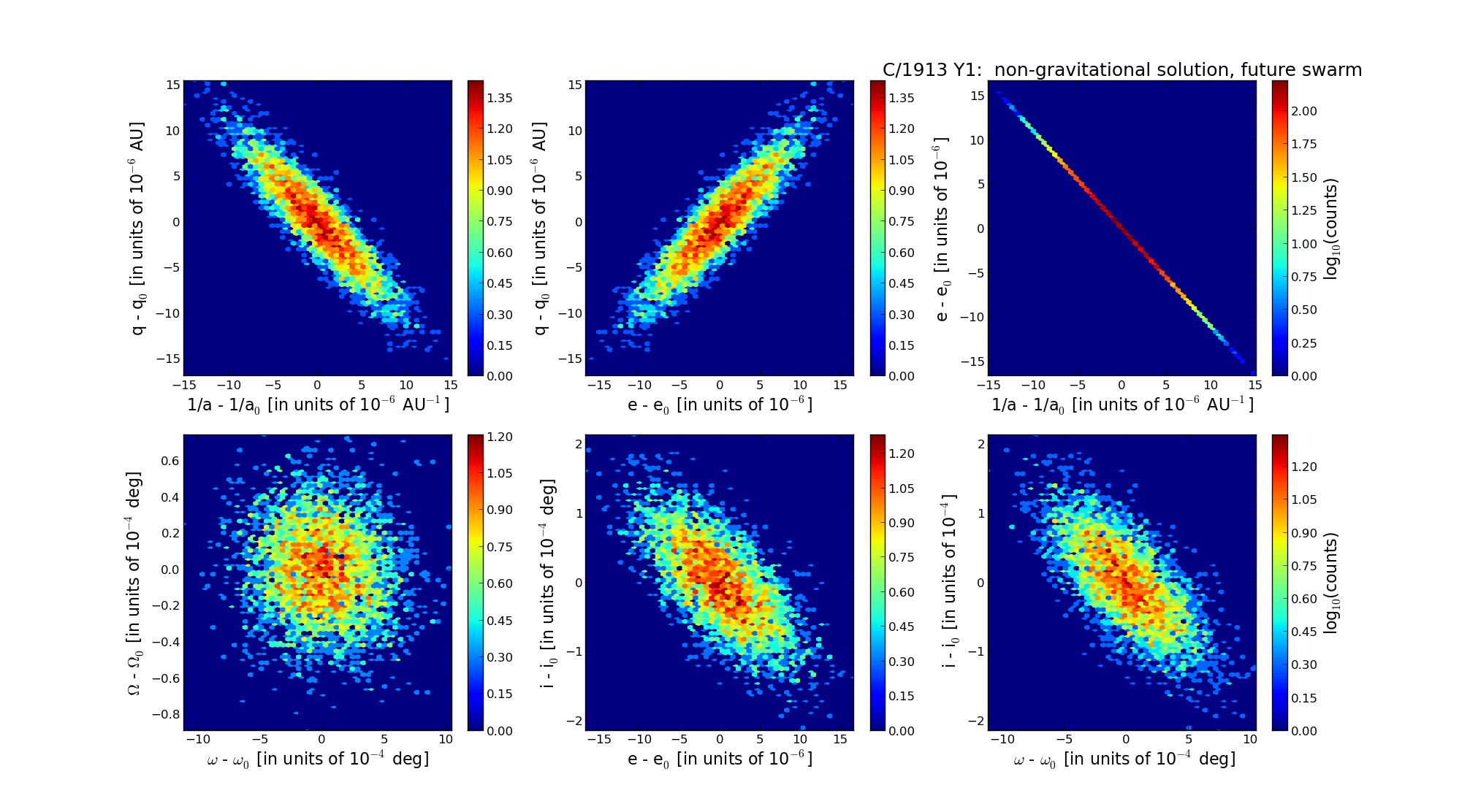
| Epoch (TT) | 22140224 | |
| time of perihelion passage (TT) | 19141026.924707 | ± 0.000072 |
| perihelion distance | 1.10515434 | ± 0.00000461 |
| eccentricity | 0.99990403 | ± 0.00000467 |
| argument of perihelion [deg] | 97.458874 | ± 0.000300 |
| longitude of the ascending node [deg] | 60.292937 | ± 0.000023 |
| inclination [deg] | 67.982497 | ± 0.000059 |
| inverse semimajor axis [10-6 au-1] | 86.84 | ± 4.23 |